MOLE REMOVAL | NYC
With two board certified dermatologists and a dermatopathologist on the team, Goldenberg Dermatology provides special expertise in the screening, diagnosis, and removal of moles.
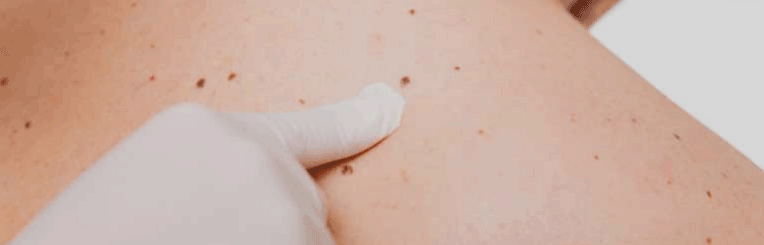
In some cases, patients simply desire to have a mole removed for aesthetic reasons because they feel it is unattractive. However, other moles need to be removed for medical reasons so that they do not develop into precancerous or cancerous (malignant) melanoma skin cancer. A mole that has changed color or shape, or is growing, bleeding, or itching should be examined by a dermatologist as soon as possible.
Goldenberg Dermatology in NYC proudly features the most advanced skin cancer technologies, including state-of-the-art, non-invasive Nevisense, an advanced method utilized for the detection of melanoma and abnormal moles (dysplastic nevi) in the earliest stages.
If you have a suspicious, unattractive, or changing growth, bump, spot, lesion, mole, or wart anywhere on your body, schedule a consultation at our Upper East Side Manhattan dermatology office to explore your treatment options with a board certified dermatologist.
Nevi and Dysplastic (Atypical) Nevi
Moles or nevi are growths on the skin. These growths occur when cells in the skin, called melanocytes, grow in a cluster with tissue surrounding them. Moles are usually pink, tan, brown, or flesh-colored. Melanocytes are also spread evenly throughout the skin and produce the pigment that gives skin its natural color. When skin is exposed to the sun, melanocytes produce more pigment, causing the skin to tan, or darken.
Moles are extremely common; most people have between 10 and 40 moles and can develop new moles usually until about age 40. Moles can be flat or raised and are usually round or oval and no larger than a pencil eraser. Many moles begin as a small, flat spot and slowly become larger in diameter and raised. Over many years, they may flatten again, become flesh-colored, and disappear.
Dysplastic Nevi
About one out of every ten people has at least one unusual (or atypical) mole that looks different from an ordinary mole, called dysplastic nevi. These lesions are abnormal, and depending on the level of abnormality (“dysplasia” or “atypia”), may need to be removed. Severely dysplastic nevi need to be completely removed (excised), to ensure they don’t progress to malignant melanoma skin cancer. Our doctors specialize in using the Nevisense device, that can help determine if a mole has a high or low risk of being a malignant melanoma skin cancer.
Removal & Excision
There are several ways to remove moles, normal or dysplastic. The doctor may initially perform a shave or punch biopsy and send the lesion for diagnosis. If the lesion is severely dysplastic, the doctor will perform a surgical excision, which requires stitching, to ensure that the entire lesion is removed and the chance of progression to cancer is eliminated.