Regular Skin Cancer Screening Can Save Your Life
As the largest organ, the skin plays in important role in protecting your body, controlling your internal temperature, and balance of water, vitamins, or minerals. It is essential to take proper care of your skin because exposure to the sun’s damaging UV rays can potentially lead to skin cancer. According to the Skin Cancer Foundation, approximately five million Americans are treated for skin cancer every year and about one in five Americans will fight skin cancer at some point in their life.
Early detection and treatment of skin cancer has been one of the most significant advances in medicine in the past decade. When detected early and removed promptly and early on, skin cancer has a very high rate of being cured. However, when skin cancers such as melanoma advance, they can be deadly. So prompt and regular skin cancer screening is necessary to ensure you life a long and healthy life.
Doctors Gary and Kristina Goldenberg are board-certified dermatologists and experts in early diagnosis and treatment of skin cancer. Dr. Gary Goldenberg is also a recognized dermatopathologist and is able to visualize what lesions would look like under the microscope, giving him a deep understanding of each lesion he examines. Goldenberg Dermatology in NYC features the most advanced skin cancer technologies, including state-of-the-art, non-invasive Nevisense, an advanced method utilized for the detection of melanoma and abnormal moles (dysplastic nevi) in the earliest stages.
Signs of Skin Cancer
Number of skin cancers has increased dramatically in recent years. This includes both melanoma and non-melanoma forms of skin cancer. Melanoma cancer originates from melanocytes, skin cells which give pigment or color to our skin. It is estimated that 1 in 50 Americans will develop melanoma in their lifetime. One patient dies from melanoma every hour. Non-melanoma skin cancers, mainly basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma, are very common. Approximately 3.5 million cases are diagnosed annually.
Skin cancer can start as an innocuous appearing spot. These lesions can grow and become symptomatic, with bleeding, crusting, scabbing, and pain. Lesions can also grow rapidly, change in size or color.
So, what are the signs of skin cancer? Non-melanoma skin cancers usually present as red, crusted, bleeding, scabbed or scaly lesions. Some lesions, especially nodular basal cell carcinoma, can look like a flesh colored bump with dilated blood vessels. These skin cancers are usually on sun exposed skin, with scalp, face, hands and forearms being the most common locations.
Melanoma can present as a new “mole” or a changing mole. These lesions are usually dark in color, but can vary in color from light brown to dark brown, black, blue or red. A rare subset of melanoma, known as amelanotic melanoma, can present as reddish or flesh color bump.
The ABCs of Skin Cancer
When examining moles, it’s important to remember the ABCDE’s:
- A is for Asymmetry: You may find that a new mole has appeared which has an irregular shape or its two halves look different from each other.
- B is for Border: The edges of the mole do not appear as they normally should. For instance, the edges are rough or blurred or jagged.
- C is for Color: Moles generally tend to be of a single color with shades of brown being the most common colors. Melanoma usually presents with multiple colors or shows color irregularity.
- D is for Diameter: Moles larger than 6 millimeters (about size of a pencil eraser) are worrisome for melanoma.
- E is for Evolving/Elevated: Moles that are changing or elevated (raised) should be checked to make sure they are not melanoma skin cancer.
Types of Skin Cancer
The three most common types of skin cancer are basal cell, squamous cell, and melanoma.
Basal cell carcinoma is the most common form of skin cancer. Starting in the basal cells of the epidermis, basal cell carcinoma usually appears as small bumps or nodules on the skin. Overtime, BCC can spread to surrounding tissues and even affect nerves and bones, causing severe damage and disfigurement. Since the major cause of BCC is chronic sun exposure, it commonly appears on areas frequently exposed to the sun such as the face, neck, arms, and shoulders but can also develop in others parts of the body. Although it can occur in all races, those with fair skin have a higher risk of developing this type of skin cancer. People who spend long hours in the sun or tan often are also more susceptible to BCC. If diagnosed early, basal cell carcinoma can be easily treated.
Squamous cell carcinoma is the second most common type of skin cancer. Occurring in the outer layer of the skin, squamous cell carcinoma is a tumor that often appears as a red firm bumps, scaly patches, or sores. SCC can occur anywhere on the body but usually form on areas that are frequently exposed to the sun such as the face, lips, scalp, ears, etc. SCC is more likely to develop in middle aged- and elderly people, especially those with fair skin complexions. Squamous cell carcinoma can grow deep in the skin and spread to other parts of the body, causing damage and disfigurement. With an early diagnosis, squamous cell carcinoma may be treated.
Melanoma is most deadly form of skin cancer. Affecting over 44,000 people in the United States each year and causes the most deaths, melanoma usually develops as a dark mole or spot on the skin. Melanoma can develop from a mole or arise as a melanoma from the start. Excessive sun exposure and UV radiation are the main causes of melanoma; however, genetics is also a key factor in developing melanoma. Those who have family members who suffer from melanoma are more susceptible to this type of skin cancer. Melanoma spreads very quickly and can become fatal; therefore, regular check-ups and early diagnosis is crucial in order to properly treat this type of skin cancer.
Depending on the stage of cancer, there are many different treatment options. Surgery is the most common treatment for skin cancer. If the cancer has not spread to other parts of the body, surgery is usually successful in removing the cancerous mass. Another treatment option is chemotherapy, which utilizes anti-cancer drugs to destroy or control the growth of cancer cells. Radiation is also a treatment option for those who suffer from cancer. Radiation therapy uses ionizing radiation to kill or control malignant cells. Other treatment options for skin cancer include photodynamic therapy, laser surgery, or topical medications.
3 Ways to Decrease Risk of Skin Cancer
Sun Protection
Sun protection is most important to prevent and decrease the risk of skin cancer. This is accomplished in several ways. Sun avoidance, such as walking on the shaded side of the street, avoiding mid-day sun, and using an umbrella at the beach are important. Wearing a wide-brimmed hat and other sun protective clothing is important. Special clothes are available for outdoor activities, such as golf or tennis, running, going to the beach and etc. These clothes have “UPF” – the fabric is woven tightly to prevent sun’s harmful rays from penetrating the article of clothes. Some new options include fabrics to keep one cool and absorb sweat. Using sunscreen is one of the cornerstones of sun protection.
Look for a trusted brand sunscreen with broad-spectrum protection, SPF 30 and above, and water resistance. Spray sunscreen have been recently criticized for not working as well if not rubbed in. The amount of sunscreen used is important – apply about a shot-glass amount each time. It’s also important to reapply regularly, about every 3 hours or so, especially after being in water or participating in a physical activity.
Yearly Skin Cancer Screening
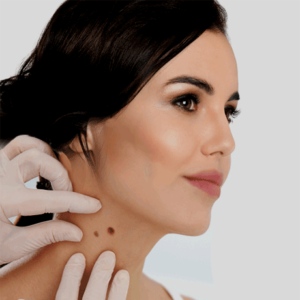
During this exam a dermatologist will check your skin from head to toe. Although skin cancer is most common on sun-exposed skin, it’s also important to check areas where “the sun don’t shine,” since some patients may develop skin cancer in those locations. This is especially true for those who’ve used tanning beds in the past. The goal of this exam is to find abnormal lesions early, either to prevent development of skin cancer or to find skin cancer when it’s least invasive. If an abnormal lesion is found, a biopsy may be performed. Depending on the results, your dermatologist may perform an additional treatment of skin cancer and ask you to follow up more often than annually.
Perform a Monthly Self Exam for Skin Cancer
A monthly self skin exam may help you find an abnormal mole or even skin cancer. Look for lesions that are new, changing in size, color or texture, or are painful, itchy or sore. While benign lesions may sometimes produce all of these changes, make sure to see your dermatologist to have the lesion checked.
When to Get Skin Cancer Screening
It is recommended that most adults have regular skin cancers screening checks – every year if possible. The American Academy of Dermatology recommends a yearly full skin check with a Board Certified Dermatologist for those 18 years old or over. And patients with a family history of skin cancer or whose skin is exposed to excessive amounts of sun – from tanning, outdoor activities, working outside, or even driving – more frequent skin cancer screenings should be conducted.
Additionally, if you are concerned about a specific spot, don’t wait for your annual skin cancer screening – get it checked as soon as possible. Depending on what the Dr. Goldenberg observes, he may decide to do a biopsy which will then confirm if there’s any cause for concern. If it turns out that the lesion is indeed cancerous, then Dr. Goldenberg will book you for surgery. The cancerous cells will be surgically cut out through excision.
Skin Cancer Screening NYC
Early diagnosis and treatment of skin cancer can typically result in a complete cure so you can continue to live a long and healthy life. But delaying skin cancer screening – especially if you have a suspicious mole, lump, bump, or lesion on the skin – can be deadly.
If you haven’t had a skin cancer screening check in the last year – or if you have a concerning spot or mole – schedule an appointment with Dr. Goldenberg for a full body skin cancer screening.
NYC Skin Cancer Screening: 212-405-8202
Dermatology & Aesthetic Blog
Thank you for visiting Goldenberg Dermatology’s Blog, where we keep you updated on the latest news, events, information, and advancements in dermatology and aesthetic treatments.
Check back often to read about the latest techniques and state-of-the-art technologies in skin health, cosmetic procedures, anti-aging, body sculpting, hair loss treatment, fat loss, and more.
Learn more about the treatments that can improve your health and quality of life – and if you have a specific concern CLICK HERE to book a consultation with one of our award winning New York board-certified dermatologists.